Face Recognition

이탤릭 볼드 이탤릭볼드
Workflow stages
- Question or problem definition.
- Acquire training and testing data.
- Wrangle, prepare, cleanse the data.
- Analyze, identify patterns, and explore the data.
- Model, predict and solve the problem.
- Visualize, report, and present the problem solving steps and final solution.
- Supply or submit the results.
기본적으로 설치되어 있어야하는 패키지는 아래 코드 를 사용한다.
import dlib, cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.patheffects as path_effects
data 가져오기
#인터넷에서 모델 다운
# - https://github.com/davisking/dlib-mod...
# - https://github.com/kairess/simple_fac...
모델 불러오기
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() # 얼굴 탐지 모델
sp = dlib.shape_predictor('models/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat') # 얼굴 랜드마크 탐지 모델
facerec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('models/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat') # 얼굴 인식 모델
함수 작성
def find_faces(img):
dets = detector(img, 1)
if len(dets) == 0: # 얼굴을 못찾으면
return np.empty(0), np.empty(0), np.empty(0) # 빈배열 반환
rects, shapes = [], []
shapes_np = np.zeros((len(dets), 68, 2), dtype=np.int) # 68개의 얼굴 landmark를 구하기
for k, d in enumerate(dets): # 얼굴의 갯수 만큼 loop
rect = ((d.left(), d.top()), (d.right(), d.bottom())) # 얼굴의 왼쪽위 , 오른쪽 아래
rects.append(rect)
shape = sp(img, d)
# convert dlib shape to numpy array
for i in range(0, 68):
shapes_np[k][i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
shapes.append(shape)
return rects, shapes, shapes_np
def encode_faces(img, shapes): # 이미지를 인코딩을 통해 128개의 벡터로 변환
face_descriptors = []
for shape in shapes:
face_descriptor = facerec.compute_face_descriptor(img, shape)
face_descriptors.append(np.array(face_descriptor))
return np.array(face_descriptors)
Compute Saved Face Descriptions
img_paths = {
'neo': 'img/neo.jpg',
'trinity': 'img/trinity.jpg',
'morpheus': 'img/morpheus.jpg',
'smith': 'img/smith.jpg'
}
descs = {
'neo': None,
'trinity': None,
'morpheus': None,
'smith': None
}
for name, img_path in img_paths.items():
img_bgr = cv2.imread(img_path) # 이미지 로드
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR -> RGB로 변환
_, img_shapes, _ = find_faces(img_rgb)
descs[name] = encode_faces(img_rgb, img_shapes)[0]
np.save('img/descs.npy', descs)
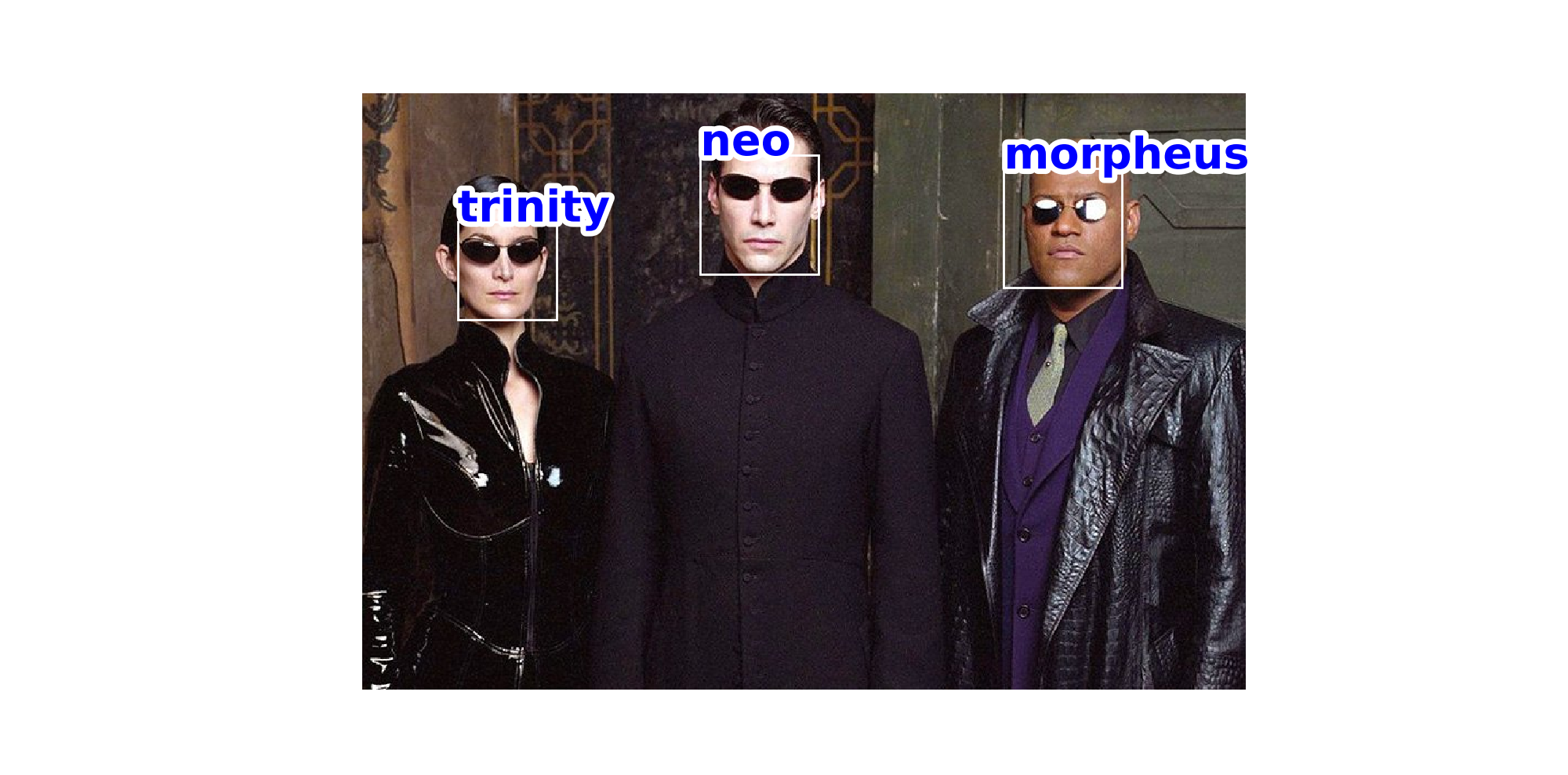
Compute Input
img_bgr = cv2.imread('img/matrix5.jpg')
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
rects, shapes, _ = find_faces(img_rgb)
descriptors = encode_faces(img_rgb, shapes)
Visualize Output
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(20, 20))
ax.imshow(img_rgb)
for i, desc in enumerate(descriptors):
found = False
for name, saved_desc in descs.items():
dist = np.linalg.norm([desc] - saved_desc, axis=1) # np.linalg.norm(a - b) a, b 벡터 사이의 유클리디안 거리를 구함
if dist < 0.6: # 0.6이 성능이 제일 좋다고 함
found = True
text = ax.text(rects[i][0][0], rects[i][0][1], name,
color='b', fontsize=40, fontweight='bold')
text.set_path_effects([path_effects.Stroke(linewidth=10, foreground='white'), path_effects.Normal()])
rect = patches.Rectangle(rects[i][0],
rects[i][1][1] - rects[i][0][1],
rects[i][1][0] - rects[i][0][0],
linewidth=2, edgecolor='w', facecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
break
if not found:
ax.text(rects[i][0][0], rects[i][0][1], 'unknown',
color='r', fontsize=20, fontweight='bold')
rect = patches.Rectangle(rects[i][0],
rects[i][1][1] - rects[i][0][1],
rects[i][1][0] - rects[i][0][0],
linewidth=2, edgecolor='r', facecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.axis('off')
plt.savefig('result/output.png')
plt.show()


