—-

이탤릭 볼드 이탤릭볼드
Workflow stages
- Question or problem definition.
- Acquire training and testing data.
- Wrangle, prepare, cleanse the data.
- Analyze, identify patterns, and explore the data.
- Model, predict and solve the problem.
- Visualize, report, and present the problem solving steps and final solution.
- Supply or submit the results.
기본적으로 설치되어 있어야하는 패키지는 아래 코드 를 사용한다.
from google.colab import auth, drive # GCP Bucket연동
from tensorflow.keras.utils import Progbar
auth.authenticate_user() # GCP 연동을 위한 인증
import re, sys, time
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules: # Colab-only Tensorflow version selector
%tensorflow_version 2.x
import tensorflow as tf
print("Tensorflow version " + tf.__version__)
AUTO = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
TPU 위치 찾기
# Detect hardware, return appropriate distribution strategy
try:
tpu = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver() # TPU detection
print('Running on TPU ', tpu.cluster_spec().as_dict()['worker'])
except ValueError:
tpu = None
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_logical_devices("GPU")
if tpu:
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(tpu)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(tpu)
strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(tpu)
elif len(gpus) > 1: # multiple GPUs in one VM
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy(gpus)
else: # default strategy that works on CPU and single GPU
strategy = tf.distribute.get_strategy()
print("REPLICAS: ", strategy.num_replicas_in_sync)
DATA SIZE 규격 정리
EPOCHS = 12
IMAGE_SIZE = [331, 331]
FLOWERS_DATASETS = { # available image sizes
192: 'gs://flowers-public/tfrecords-jpeg-192x192-2/*.tfrec',
224: 'gs://flowers-public/tfrecords-jpeg-224x224/*.tfrec',
331: 'gs://flowers-public/tfrecords-jpeg-331x331/*.tfrec',
512: 'gs://flowers-public/tfrecords-jpeg-512x512/*.tfrec'
}
CLASSES = ['daisy', 'dandelion', 'roses', 'sunflowers', 'tulips'] # do not change, maps to the labels in the data (folder names)
assert IMAGE_SIZE[0] == IMAGE_SIZE[1], "only square images are supported"
assert IMAGE_SIZE[0] in FLOWERS_DATASETS, "this image size is not supported"
DATA SIZE 규격 정리
# TPU에서 자동으로 bfloat16을 사용. 해당 format을 사용시 혼합 정밀도 학습의 성능 및 메모리 데이터가 줄어들어 효율성이 좋음
# https://cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/bfloat16?hl=ko
MIXED_PRECISION = False
if MIXED_PRECISION:
if tpu:
policy = tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental.Policy('mixed_bfloat16')
else: #
policy = tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental.Policy('mixed_float16')
tf.config.optimizer.set_jit(True) # XLA compilation
tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental.set_policy(policy)
print('Mixed precision enabled')
배치 및 학습률 세팅
# batch and learning rate settings
if strategy.num_replicas_in_sync == 8: # TPU or 8xGPU
BATCH_SIZE = 16 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
VALIDATION_BATCH_SIZE = 16 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
start_lr = 0.00001
min_lr = 0.00001
max_lr = 0.00005 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
rampup_epochs = 5
sustain_epochs = 0
exp_decay = .8
elif strategy.num_replicas_in_sync == 1: # single GPU
BATCH_SIZE = 16
VALIDATION_BATCH_SIZE = 16
start_lr = 0.00001
min_lr = 0.00001
max_lr = 0.0002
rampup_epochs = 5
sustain_epochs = 0
exp_decay = .8
else: # TPU pod
BATCH_SIZE = 8 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
VALIDATION_BATCH_SIZE = 8 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
start_lr = 0.00001
min_lr = 0.00001
max_lr = 0.00002 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
rampup_epochs = 7
sustain_epochs = 0
exp_decay = .8
def lrfn(epoch):
def lr(epoch, start_lr, min_lr, max_lr, rampup_epochs, sustain_epochs, exp_decay):
if epoch < rampup_epochs:
lr = (max_lr - start_lr)/rampup_epochs * epoch + start_lr
elif epoch < rampup_epochs + sustain_epochs:
lr = max_lr
else:
lr = (max_lr - min_lr) * exp_decay**(epoch-rampup_epochs-sustain_epochs) + min_lr
return lr
return lr(epoch, start_lr, min_lr, max_lr, rampup_epochs, sustain_epochs, exp_decay)
lr_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(lambda epoch: lrfn(epoch), verbose=True)
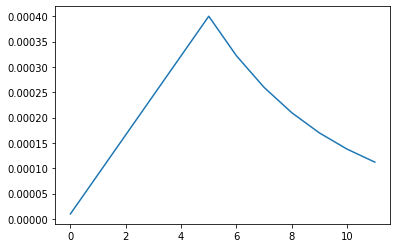
rng = [i for i in range(EPOCHS)]
y = [lrfn(x) for x in rng]
plt.plot(rng, [lrfn(x) for x in rng])
print(y[0], y[-1])
이미지 라벨 읽기
def count_data_items(filenames):
# the number of data items is written in the name of the .tfrec files, i.e. flowers00-230.tfrec = 230 data items
n = [int(re.compile(r"-([0-9]*)\.").search(filename).group(1)) for filename in filenames]
return np.sum(n)
gcs_pattern = FLOWERS_DATASETS[IMAGE_SIZE[0]]
validation_split = 0.19
filenames = tf.io.gfile.glob(gcs_pattern) # A list of strings containing filenames that match the given pattern(s)
split = len(filenames) - int(len(filenames) * validation_split) # 전체 이미지 갯수에서 19% 만큼 분리함
TRAIN_FILENAMES = filenames[:split] # train 셋
VALID_FILENAMES = filenames[split:] # test 셋
TRAIN_STEPS = count_data_items(TRAIN_FILENAMES) // BATCH_SIZE # 학습 데이터를 배치로 나누어줌
print("TRAINING IMAGES: ", count_data_items(TRAIN_FILENAMES), ", STEPS PER EPOCH: ", TRAIN_STEPS)
print("VALIDATION IMAGES: ", count_data_items(VALID_FILENAMES))
데이터 처리
def read_tfrecord(example): # 데이터 파싱. 0~255 data를 0~1로 바꿈
features = {
"image": tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), # tf.string means bytestring
"class": tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), # shape [] means scalar
"one_hot_class": tf.io.VarLenFeature(tf.float32),
}
example = tf.io.parse_single_example(example, features)
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(example['image'], channels=3)
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255.0 # convert image to floats in [0, 1] range
class_label = tf.cast(example['class'], tf.int32)
one_hot_class = tf.sparse.to_dense(example['one_hot_class'])
one_hot_class = tf.reshape(one_hot_class, [5])
return image, one_hot_class
def force_image_sizes(dataset, image_size):
# explicit size will be needed for TPU
reshape_images = lambda image, label: (tf.reshape(image, [*image_size, 3]), label)
dataset = dataset.map(reshape_images, num_parallel_calls=AUTO)
return dataset
def load_dataset(filenames):
# read from TFRecords. For optimal performance, use "interleave(tf.data.TFRecordDataset, ...)"
# to read from multiple TFRecord files at once and set the option experimental_deterministic = False
# to allow order-altering optimizations.
opt = tf.data.Options()
opt.experimental_deterministic = False
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(filenames)
dataset = dataset.with_options(opt)
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(filenames, num_parallel_reads=AUTO) # 여러 파일에서 읽은 내용을 자동으로 interleaves
dataset = dataset.map(read_tfrecord, num_parallel_calls=AUTO)
dataset = force_image_sizes(dataset, IMAGE_SIZE)
return dataset
def data_augment(image, one_hot_class):
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image) # 4-D Tensor of shape [batch, height, width, channels] or 3-D Tensor of shape [height, width, channels].
image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, 0, 2) # Equivalent to adjust_saturation() but uses a saturation_factor randomly picked in the interval [lower, upper].
return image, one_hot_class
def get_training_dataset():
dataset = load_dataset(TRAIN_FILENAMES)
dataset = dataset.map(data_augment, num_parallel_calls=AUTO)
dataset = dataset.repeat()
dataset = dataset.shuffle(2048)
dataset = dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(AUTO) # prefetch next batch while training (autotune prefetch buffer size)
return dataset
def get_validation_dataset():
dataset = load_dataset(VALID_FILENAMES)
dataset = dataset.batch(VALIDATION_BATCH_SIZE)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(AUTO) # prefetch next batch while training (autotune prefetch buffer size)
# needed for TPU 32-core pod: the test dataset has only 3 files but there are 4 TPUs. FILE sharding policy must be disabled.
opt = tf.data.Options()
opt.experimental_distribute.auto_shard_policy = tf.data.experimental.AutoShardPolicy.DATA
dataset = dataset.with_options(opt)
return dataset
data셋 가져오기
training_dataset = get_training_dataset()
validation_dataset = get_validation_dataset()
data셋 보여주기
# If model is provided, use it to generate predictions.
def display_nine_flowers(images, titles, title_colors=None):
subplot = 331
plt.figure(figsize=(13,13))
for i in range(9):
color = 'black' if title_colors is None else title_colors[i]
display_one_flower(images[i], titles[i], 331+i, color)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.1, hspace=0.1)
plt.show()
def get_dataset_iterator(dataset, n_examples):
return dataset.unbatch().batch(n_examples).as_numpy_iterator()
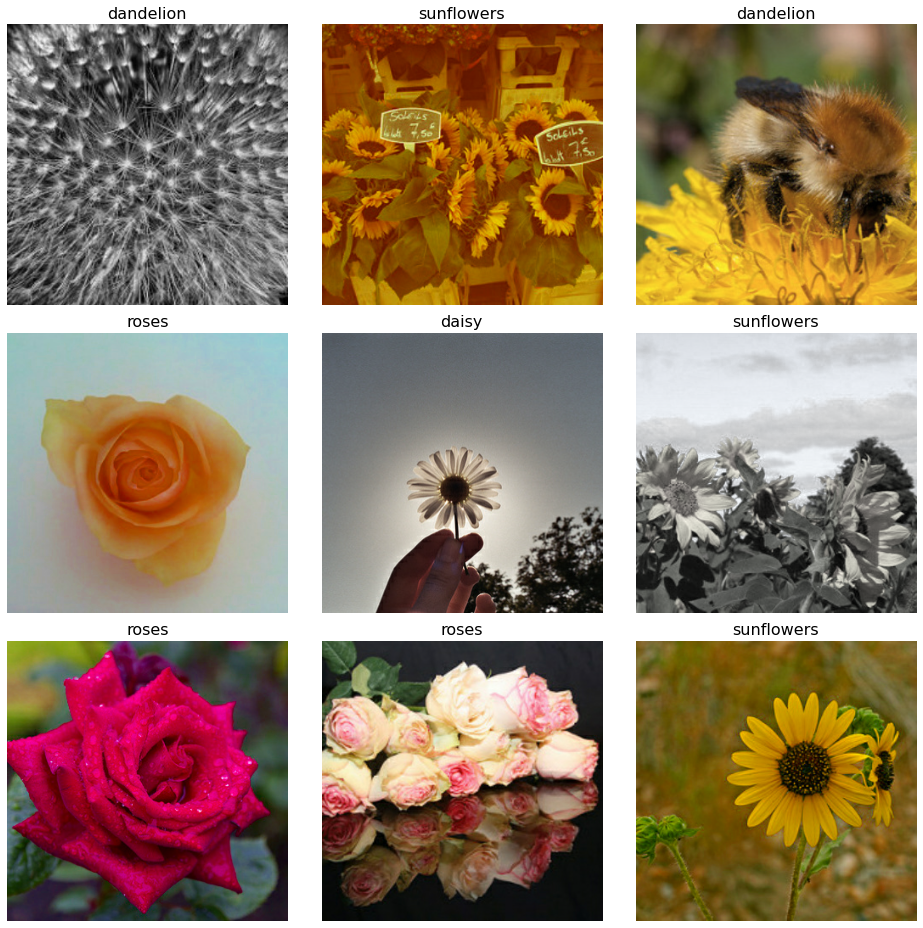
training_viz_iterator = get_dataset_iterator(training_dataset, 9)
# Re-run this cell to show a new batch of images
images, classes = next(training_viz_iterator)
class_idxs = np.argmax(classes, axis=-1) # transform from one-hot array to class number
labels = [CLASSES[idx] for idx in class_idxs]
display_nine_flowers(images, labels)

모델 생성
def create_model():
#pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2(input_shape=[*IMAGE_SIZE, 3], include_top=False)
pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.Xception(input_shape=[*IMAGE_SIZE, 3], include_top=False)
#pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False ,input_shape=[*IMAGE_SIZE, 3])
#pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.ResNet50(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=[*IMAGE_SIZE, 3])
#pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.MobileNet(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=[*IMAGE_SIZE, 3])
pretrained_model.trainable = True
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
pretrained_model,
tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(),
#tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation='softmax', dtype=tf.float32) # the float32 is needed on softmax layer when using mixed precision
])
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss = 'categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
return model
TPU 사용해서 모델 감싸기
with strategy.scope(): # creating the model in the TPUStrategy scope places the model on the TPU
model = create_model()
model.summary()
학습
start_time = time.time()
history = model.fit(training_dataset, validation_data=validation_dataset,
steps_per_epoch=TRAIN_STEPS, epochs=EPOCHS, callbacks=[lr_callback])
final_accuracy = history.history["val_accuracy"][-5:]
print("FINAL ACCURACY MEAN-5: ", np.mean(final_accuracy))
print("TRAINING TIME: ", time.time() - start_time, " sec")
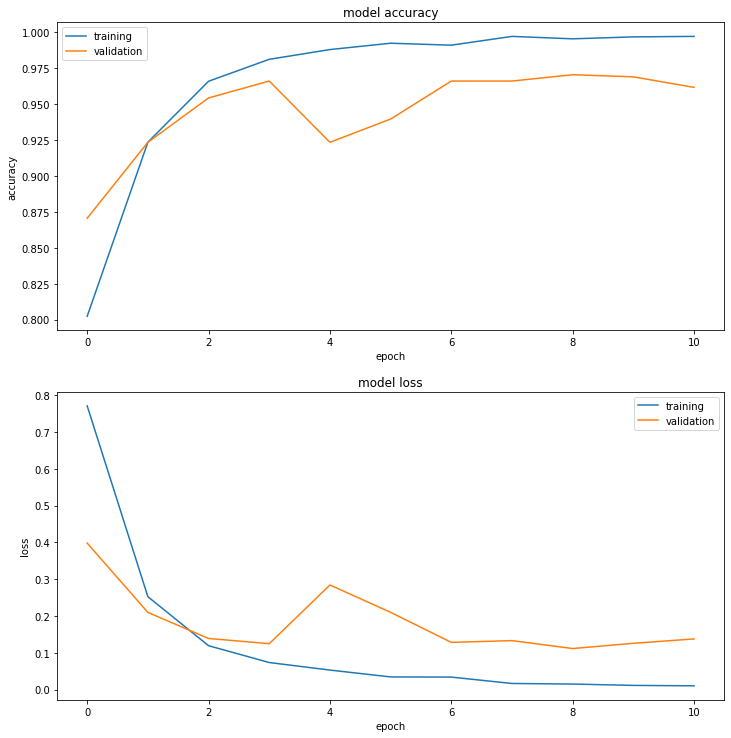
def display_training_curves(training, validation, title, subplot):
ax = plt.subplot(subplot)
ax.plot(training)
ax.plot(validation)
ax.set_title('model '+ title)
ax.set_ylabel(title)
ax.set_xlabel('epoch')
ax.legend(['training', 'validation'])
print(history.history.keys())
plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10)) # 그림이 너무 작으니 좀 키워줌
plt.tight_layout() # 그림이 너무 작으니 좀 키워줌
display_training_curves(history.history['accuracy'][1:], history.history['val_accuracy'][1:], 'accuracy', 211)
display_training_curves(history.history['loss'][1:], history.history['val_loss'][1:], 'loss', 212)
예측
def flower_title(label, prediction):
# Both prediction (probabilities) and label (one-hot) are arrays with one item per class.
class_idx = np.argmax(label, axis=-1)
prediction_idx = np.argmax(prediction, axis=-1)
if class_idx == prediction_idx:
return f'{CLASSES[prediction_idx]} [correct]', 'black'
else:
return f'{CLASSES[prediction_idx]} [incorrect, should be {CLASSES[class_idx]}]', 'red'
def get_titles(images, labels, model):
predictions = model.predict(images)
titles, colors = [], []
for label, prediction in zip(classes, predictions):
title, color = flower_title(label, prediction)
titles.append(title)
colors.append(color)
return titles, colors
validation_viz_iterator = get_dataset_iterator(validation_dataset, 9)
# Re-run this cell to show a new batch of images
images, classes = next(validation_viz_iterator)
titles, colors = get_titles(images, classes, model)
display_nine_flowers(images, titles, colors)

모델 저장
# We can save our model with:
model.save('model.h5')
# and reload it with:
reloaded_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('model.h5')
# Re-run this cell to show a new batch of images
images, classes = next(validation_viz_iterator)
titles, colors = get_titles(images, classes, reloaded_model)
display_nine_flowers(images, titles, colors)

