—-

이탤릭 볼드 이탤릭볼드
Workflow stages
- Question or problem definition.
- Acquire training and testing data.
- Wrangle, prepare, cleanse the data.
- Analyze, identify patterns, and explore the data.
- Model, predict and solve the problem.
- Visualize, report, and present the problem solving steps and final solution.
- Supply or submit the results.
기본적으로 설치되어 있어야하는 패키지는 아래 코드 를 사용한다.
from google.colab import auth, drive # GCP Bucket연동
from tensorflow.keras.utils import Progbar
auth.authenticate_user() # GCP 연동을 위한 인증
import re, sys, time
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules: # Colab-only Tensorflow version selector
%tensorflow_version 2.x
import tensorflow as tf
print("Tensorflow version " + tf.__version__)
AUTO = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
GCP Bucket 연동
!git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/gcsfuse.git
!echo "deb http://packages.cloud.google.com/apt gcsfuse-bionic main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gcsfuse.list
!curl https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
!apt -qq update
!apt -qq install gcsfuse
Bucket에서 Colab으로 Data를 가져오기 위한 폴더 생성 및 Bucket 지정 Bucket안에 Kaggle API Key 있는지 확인
!mkdir folderOnColab
!gcsfuse bskim_kaggle_bucket folderOnColab
kaggle API에 Kaggle Key를 이동
!mkdir -p ~/.kaggle
!mv folderOnColab/kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/
!chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
Data 셋 가져오기
!wget --show-progress --continue -O /content/shakespeare.txt http://www.gutenberg.org/files/100/100-0.txt
!head -n5 /content/shakespeare.txt
!echo "..."
!shuf -n5 /content/shakespeare.txt
TPU 연동
import re, sys, time
import numpy as np
import os
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules: # Colab-only Tensorflow version selector
%tensorflow_version 2.x
import tensorflow as tf
print("Tensorflow version " + tf.__version__)
AUTO = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
# Detect hardware, return appropriate distribution strategy
try:
tpu = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver() # TPU detection
print('Running on TPU ', tpu.cluster_spec().as_dict()['worker'])
except ValueError:
tpu = None
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_logical_devices("GPU")
if tpu:
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(tpu)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(tpu)
strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(tpu)
elif len(gpus) > 1: # multiple GPUs in one VM
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy(gpus)
else: # default strategy that works on CPU and single GPU
strategy = tf.distribute.get_strategy()
print("REPLICAS: ", strategy.num_replicas_in_sync)
import distutils # 버전딸리는것들 찾기
if distutils.version.LooseVersion(tf.__version__) < '1.14':
raise Exception('This notebook is compatible with TensorFlow 1.14 or higher, for TensorFlow 1.13 or lower please use the previous version at https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/r1.13/tools/colab/shakespeare_with_tpu_and_keras.ipynb')
DATA SIZE 규격 정리
# This address identifies the TPU we'll use when configuring TensorFlow.
TPU_WORKER = 'grpc://' + os.environ['COLAB_TPU_ADDR']
SHAKESPEARE_TXT = '/content/shakespeare.txt'
def transform(txt):
return np.asarray([ord(c) for c in txt if ord(c) < 255], dtype=np.int32)
def input_fn(seq_len=100, batch_size=1024):
"""Return a dataset of source and target sequences for training."""
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(SHAKESPEARE_TXT, 'r') as f:
txt = f.read()
source = tf.constant(transform(txt), dtype=tf.int32)
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(source).batch(seq_len+1, drop_remainder=True)
def split_input_target(chunk):
input_text = chunk[:-1]
target_text = chunk[1:]
return input_text, target_text
BUFFER_SIZE = 10000
ds = ds.map(split_input_target).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)
return ds.repeat()
모델 생성
EMBEDDING_DIM = 512
def lstm_model(seq_len=100, batch_size=None, stateful=True):
"""Language model: predict the next word given the current word."""
source = tf.keras.Input(
name='seed', shape=(seq_len,), batch_size=batch_size, dtype=tf.int32)
embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(input_dim=256, output_dim=EMBEDDING_DIM)(source)
lstm_1 = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(EMBEDDING_DIM, stateful=stateful, return_sequences=True)(embedding)
lstm_2 = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(EMBEDDING_DIM, stateful=stateful, return_sequences=True)(lstm_1)
predicted_char = tf.keras.layers.TimeDistributed(tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='softmax'))(lstm_2)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[source], outputs=[predicted_char])
TPU 사용해서 모델 감싸서 학습
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
resolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver(TPU_WORKER)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(resolver)
strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(resolver)
with strategy.scope():
training_model = lstm_model(seq_len=100, stateful=False)
training_model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(learning_rate=0.01),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
training_model.fit(
input_fn(),
steps_per_epoch=100,
epochs=10
)
training_model.save_weights('/tmp/bard.h5', overwrite=True)
모델 저장 및 Bucket 저장
training_model.save_weights('/tmp/bard.h5', overwrite=True)
!gsutil cp /tmp/bard.h5 gs://bskim_bucket/model_example/
예측
BATCH_SIZE = 5
PREDICT_LEN = 250
# Keras requires the batch size be specified ahead of time for stateful models.
# We use a sequence length of 1, as we will be feeding in one character at a
# time and predicting the next character.
prediction_model = lstm_model(seq_len=1, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, stateful=True)
prediction_model.load_weights('/tmp/bard.h5')
# We seed the model with our initial string, copied BATCH_SIZE times
seed_txt = 'Looks it not like the king? Verily, we must go! '
seed = transform(seed_txt)
seed = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(seed, 0), BATCH_SIZE, axis=0)
# First, run the seed forward to prime the state of the model.
prediction_model.reset_states()
for i in range(len(seed_txt) - 1):
prediction_model.predict(seed[:, i:i + 1])
# Now we can accumulate predictions!
predictions = [seed[:, -1:]]
for i in range(PREDICT_LEN):
last_word = predictions[-1]
next_probits = prediction_model.predict(last_word)[:, 0, :]
# sample from our output distribution
next_idx = [
np.random.choice(256, p=next_probits[i])
for i in range(BATCH_SIZE)
]
predictions.append(np.asarray(next_idx, dtype=np.int32))
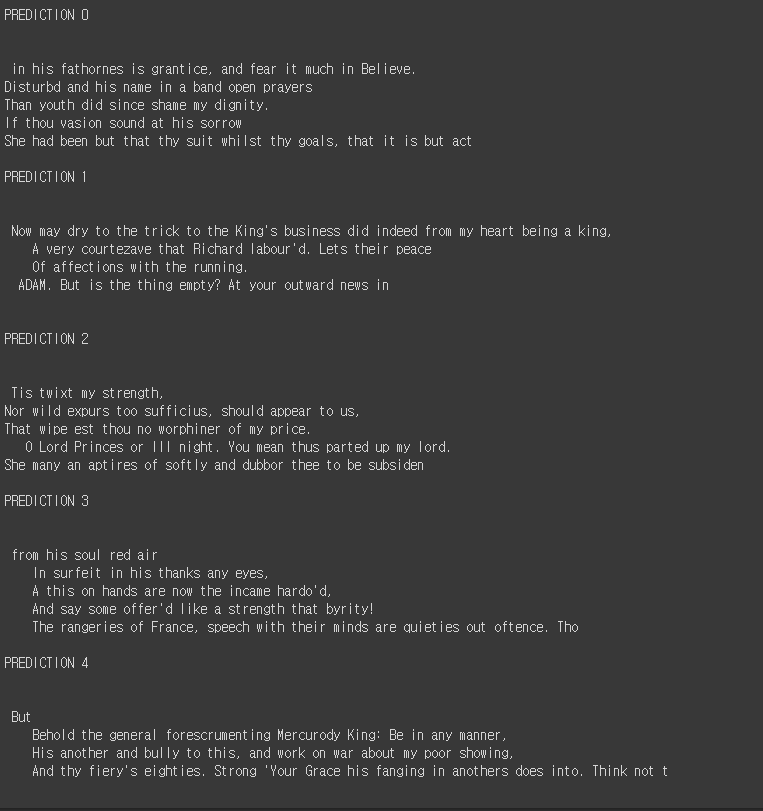
for i in range(BATCH_SIZE):
print('PREDICTION %d\n\n' % i)
p = [predictions[j][i] for j in range(PREDICT_LEN)]
generated = ''.join([chr(c) for c in p]) # Convert back to text
print(generated)
print()
assert len(generated) == PREDICT_LEN, 'Generated text too short'