Home Prices Prediction Tutorial
https://www.kaggle.com/pmarcelino/comprehensive-data-exploration-with-python

이탤릭 볼드 이탤릭볼드
Workflow stages
- Question or problem definition.
- Acquire training and testing data.
- Wrangle, prepare, cleanse the data.
- Analyze, identify patterns, and explore the data.
- Model, predict and solve the problem.
- Visualize, report, and present the problem solving steps and final solution.
- Supply or submit the results.
기본적으로 설치되어 있어야하는 패키지는 아래 코드 를 사용한다.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from time import sleep
# visualization
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# machine learning
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC, LinearSVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
data 가져오기
Train_Dir = 'training.csv'
Test_Dir = 'test.csv'
lookid_dir = 'IdLookupTable.csv'
train_data = pd.read_csv(Train_Dir)
test_data = pd.read_csv(Test_Dir)
lookid_data = pd.read_csv(lookid_dir)
data를 찍어보면 다음과 같이 나온다
print(train_data.head().T)
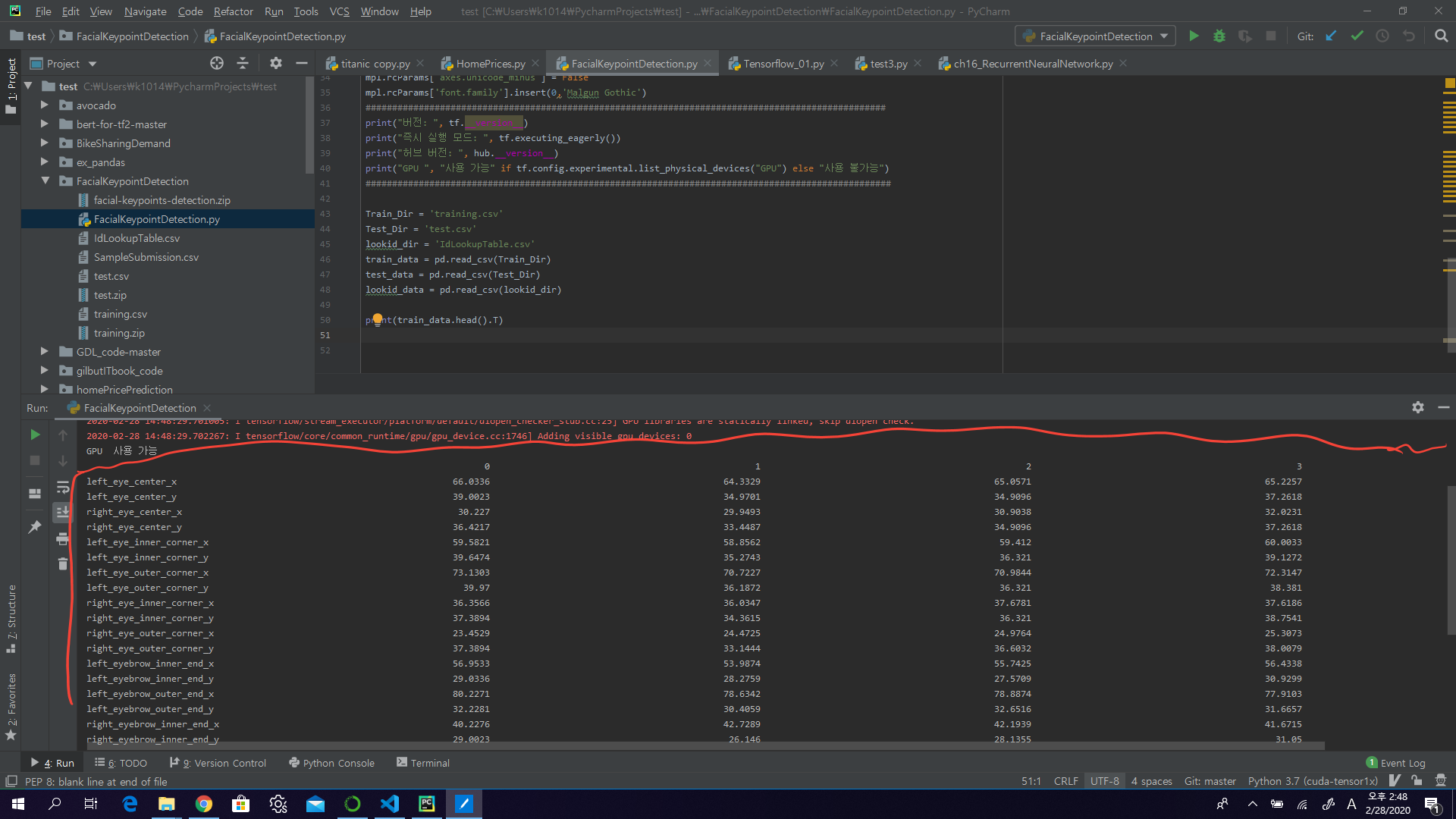
위와같은 카테고리로 되어있으며 data를 몇개 찍어보면 다음과 같다.
누락데이터 확인
print(train_data.isnull().any().value_counts())
True 28
False 3
dtype: int64
누락된 값 대체
train_data.fillna(method = 'ffill',inplace = True)
#train_data.reset_index(drop = True,inplace = True)
fillna 에 method를 ffill을 사용하여 이전 index의 값으로 누락값을 대체해준다. 다음 인덱스값으로 대체하려면 bfill을 사용하여 대체한다. False 31
dtype: int64
이미지 값 처리
현재 이미지 값이 238 236 237 238 240 240 239 241 241 243 240 23… 같은 형태로 되어있는데 이를 ‘ ‘(공백)을 기준으로 읽을 수 있도록 재 처리해준다.
imag = []
for i in range(0,7049):
img = train_data['Image'][i].split(' ')
img = ['0' if x == '' else x for x in img]
imag.append(img)
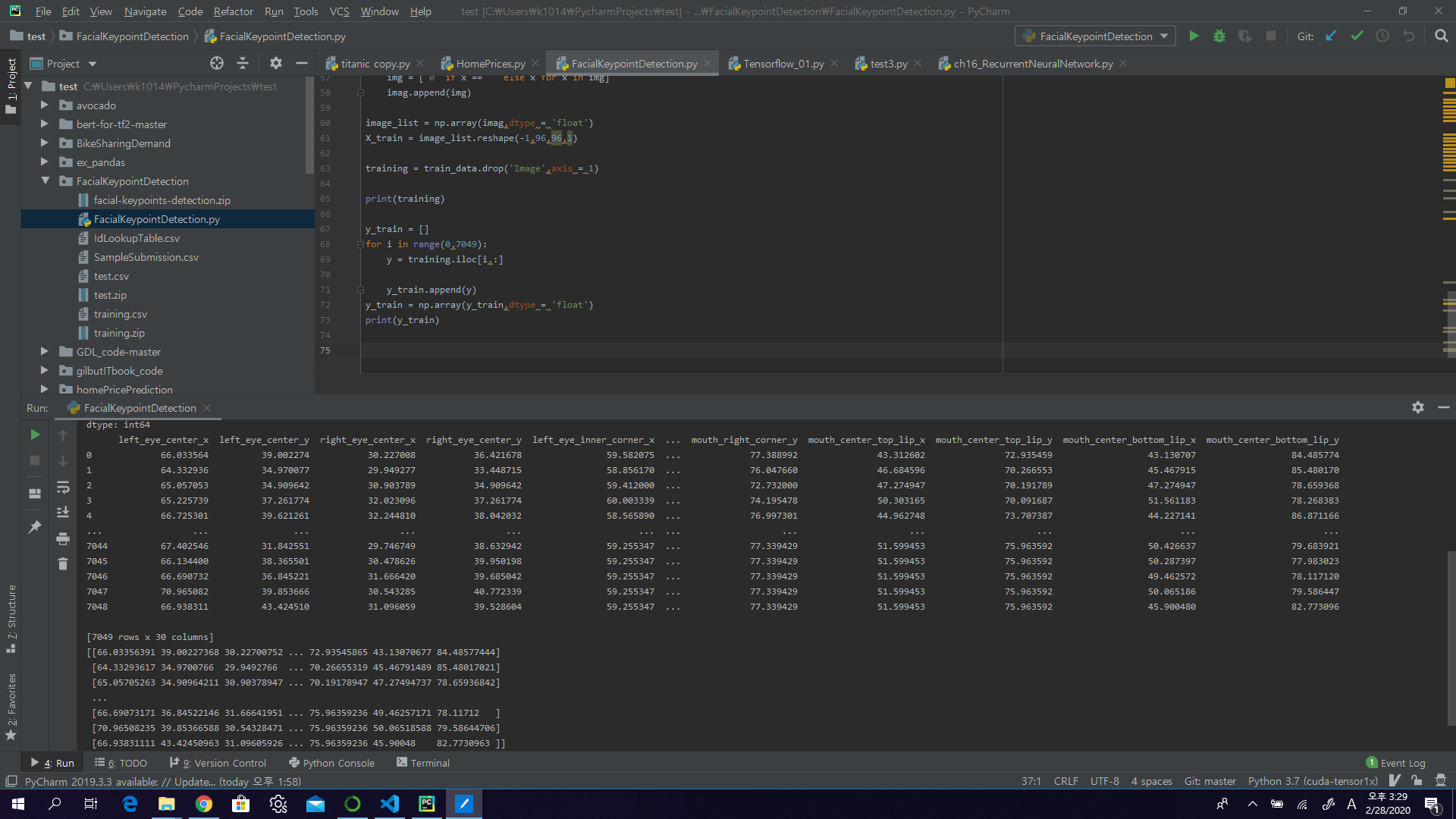
다음 처리된 이미지를 numpy를 이용하여 reshape를 해준다.
image_list = np.array(imag,dtype = 'float')
X_train = image_list.reshape(-1,96,96,1)
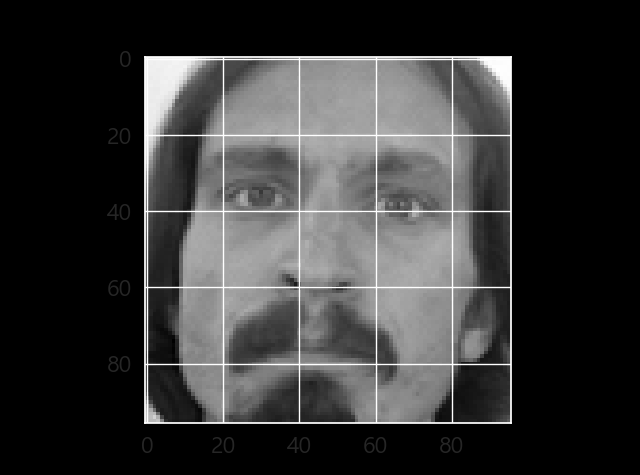
plt.imshow(X_train[0].reshape(96,96),cmap='gray')
plt.show()

라벨 분리
y_train에 원 데이터에서 이미지를 제거하고 라벨만을 분리해서 넣어준다.
training = train_data.drop('Image',axis = 1)
y_train = []
for i in range(0,7049):
y = training.iloc[i,:]
y_train.append(y)
y_train = np.array(y_train,dtype = 'float')
모델 구성
신경망의 기본 구성 요소는 층(layer)입니다. 층은 주입된 데이터에서 표현을 추출합니다. 아마도 문제를 해결하는데 더 의미있는 표현이 추출될 것입니다.
대부분 딥러닝은 간단한 층을 연결하여 구성됩니다. tf.keras.layers.Dense와 같은 층들의 가중치(parameter)는 훈련하는 동안 학습됩니다.
model = tf.keras.Sequential([tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(96,96)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.1),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30)
])
이 네트워크의 첫 번째 층인 tf.keras.layers.Flatten은 2차원 배열(96 x 96 픽셀)의 이미지 포맷을 96 * 96 = 9216 픽셀의 1차원 배열로 변환합니다. 이 층은 이미지에 있는 픽셀의 행을 펼쳐서 일렬로 늘립니다. 이 층에는 학습되는 가중치가 없고 데이터를 변환하기만 합니다.
픽셀을 펼친 후에는 두 개의 tf.keras.layers.Dense 층이 연속되어 연결됩니다. 이 층을 밀집 연결(densely-connected) 또는 완전 연결(fully-connected) 층이라고 부릅니다. 첫 번째 Dense 층은 128개의 노드(또는 뉴런)를 가집니다. 두 번째 (마지막) 층은 30개의 노드의 relu(relu) 층입니다. 이 층은 30개의 확률을 반환하고 반환된 값의 전체 합은 1입니다. 각 노드는 현재 이미지가 30개 클래스 중 하나에 속할 확률을 출력합니다.
모델 컴파일
모델을 훈련하기 전에 필요한 몇 가지 설정이 모델 컴파일 단계에서 추가됩니다:
- 손실 함수(Loss function)-훈련 하는 동안 모델의 오차를 측정합니다. 모델의 학습이 올바른 방향으로 향하도록 이 함수를 최소화해야 합니다.
- 옵티마이저(Optimizer)-데이터와 손실 함수를 바탕으로 모델의 업데이트 방법을 결정합니다.
- 지표(Metrics)-훈련 단계와 테스트 단계를 모니터링하기 위해 사용합니다. 다음 예에서는 올바르게 분류된 이미지의 비율인 정확도를 사용합니다.
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mean_squared_error', metrics=['mae'])
모델 훈련
신경망 모델을 훈련하는 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
- 훈련 데이터를 모델에 주입합니다
- 모델이 이미지와 레이블을 매핑하는 방법을 배웁니다.
- 테스트 세트에 대한 모델의 예측을 만듭니다-이 예에서는 test_images 배열입니다. 이 예측이 test_labels 배열의 레이블과 맞는지 확인합니다.
- 훈련을 시작하기 위해 model.fit 메서드를 호출하면 모델이 훈련 데이터를 학습합니다:
model.fit(X_train,y_train,epochs = 50,batch_size = 256,validation_split = 0.2)256 batch size로 50 에폭만큼 train을 수행
모델 테스트
#preparing test data
timag = []
for i in range(0,1783):
timg = test_data['Image'][i].split(' ')
timg = ['0' if x == '' else x for x in timg]
timag.append(timg)
테스트 이미지를 모델에 테스트 할 수 있도록 변환
timage_list = np.array(timag,dtype = 'float')
X_test = timage_list.reshape(-1,96,96,1)
이미지 확인
plt.imshow(X_test[0].reshape(96,96),cmap = 'gray')
plt.show()
결과 확인
pred = model.predict(X_test)
제출 format으로 csv파일 내보내기
lookid_list = list(lookid_data['FeatureName'])
imageID = list(lookid_data['ImageId']-1)
pre_list = list(pred)
rowid = lookid_data['RowId']
rowid=list(rowid)
feature = []
for f in list(lookid_data['FeatureName']):
feature.append(lookid_list.index(f))
preded = []
for x,y in zip(imageID,feature):
preded.append(pre_list[x][y])
rowid = pd.Series(rowid,name = 'RowId')
loc = pd.Series(preded,name = 'Location')
submission = pd.concat([rowid,loc],axis = 1)
submission.to_csv('face_key_detection_submission.csv',index = False)

